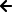This reference describes a production‑grade architecture for deploying real‑time voice assistants using Exotel’s telephony infrastructure and LiveKit’s Agent SDK. It is based on industry benchmarks that require <800 ms end‑to‑end latency[1] and leverages Exotel AgentStream (<20 ms media latency)[2] along with fast ASR, LLM and TTS services.
High‑Level Components
- Caller / PSTN network – customers dial or receive calls over the public telephone network.
- Exotel telephony layer – receives PSTN calls via a local carrier and forwards them to the LiveKit SIP endpoint. For outbound calls, Exotel dials the customer and bridges the call into LiveKit.
- LiveKit SIP Bridge – registers a SIP trunk and bridges telephony participants into a LiveKit room. Dispatch rules route calls to the appropriate agent instance[3].
- Voice Agent (LiveKit Agent) – runs on your infrastructure, joins the LiveKit room via WebRTC, and handles the conversation. The agent integrates with ASR, LLM and TTS services using streaming APIs.
- AI Services – providers such as Deepgram (150 ms TTFT)[4], ElevenLabs (<75 ms TTS)[5] and a hosted LLM (e.g., OpenAI, Groq) process speech, generate responses and synthesize speech.
- Observability & Logging – metrics collection for latency, errors and quality of service. Use Prometheus/Grafana or Exotel’s call logs.
Call Flow
Inbound Call
- Dial: A caller dials your Exotel number.
- Trunk Mapping: Exotel forwards the call to the configured SIP FQDN for your LiveKit project.
- Room Creation: LiveKit creates a new room with a prefixed name (e.g., call-<uuid>) based on your dispatch rule and invites your agent.
- Agent Join: The agent joins the room via WebRTC using the Agents SDK. It receives real‑time audio frames via AgentStream and sends back its responses.
- AI Processing: The agent streams audio to the ASR, executes the LLM prompt and synthesizes speech. Parallelised architecture with fast TTS/ASR helps achieve sub‑800 ms latency.
- Reply: The agent replies using generate_reply or by sending audio frames back to Exotel via the LiveKit room. The Exotel SIP trunk sends the response audio to the caller.
Outbound Call
- Agent Dispatch: You dispatch an agent with metadata specifying the destination phone number.
- Dial: The agent uses LiveKit’s SIP API to create a SIP participant for the outbound trunk.
- Bridge: Exotel dials the destination number and connects the call into the LiveKit room.
- Conversation: Same as inbound call; the agent handles the dialogue.
Latency Budget
| Stage | Typical Latency (ms) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Media transport (Exotel ↔ LiveKit) | <20 ms | Exotel’s AgentStream provides sub‑20 ms streaming latency. |
| ASR (Deepgram) | 150–350 ms | 150 ms TTFT in the US; ~250–350 ms internationally. |
| LLM inference | 200–300 ms | Varies with model size and hardware (use a fast LLM provider or GPU). |
| TTS (ElevenLabs Flash v2.5) | 75 ms | ElevenLabs returns first audio token in ~75 ms. |
| Total | ~550–750 ms | Parallel ASR/LLM/TTS processing enables sub‑800 ms conversational latency. |
To keep total latency within 800 ms, use streaming APIs and parallel processing. For example, start generating the TTS output before the LLM finishes to overlap computation.
Scaling & Reliability
- Horizontal scaling: Deploy multiple agent instances behind LiveKit’s dispatch rules. Rooms can hold multiple participants; use a load‑balancer to distribute agent sessions.
- High availability: Host your agent servers close to Exotel PoPs (e.g., in the same region). Deploy redundant LiveKit server clusters if self‑hosting.
- Monitoring: Collect metrics such as TimeToFirstToken, P95/P99 round‑trip latency, call drop rates, and network jitter. Use Exotel call logs and LiveKit events.
- Fallback & Transfer: Implement fallback logic to transfer calls to a human agent if the AI agent fails to respond within a threshold (e.g., 1 s). LiveKit supports transferring the SIP participant to another number.
Sample Infrastructure Diagram
+-------------+ +---------+ +----------+ +-------------+
| Caller | PSTN | Exotel | SIP | LiveKit | WebRTC | AI Agent |
| (Phone) | <----> | vSIP | <----> | SIP | <----> | (Compute) |
| | | Trunk | | Bridge | | |
+-------------+ +---------+ +----------+ +-------------+
| | |
+-----------+ | +-----------+
| ASR LLM TTS |
+--------------------------------+
The caller connects to Exotel via PSTN. Exotel routes the call to a LiveKit SIP bridge. LiveKit hosts a room that includes both the caller (SIP participant) and the AI agent (WebRTC participant). The agent communicates with ASR, LLM and TTS services to understand and respond to the caller.
Implementation Recommendations
- Use the Exotel AgentStream to stream raw audio to your agent; avoid high‑latency REST calls.
- Optimize LLM prompts and model size to reduce inference latency. For simple IVR tasks, small local models may suffice.
- Choose regionally‑closer ASR/TTS providers or self‑host models to avoid transoceanic latency.
- Instrument time stamps at each processing stage (incoming audio, ASR start, LLM start, TTS start) to monitor latency budget.
- Comply with telecom regulations in India/APAC by routing calls through Exotel’s licensed network.
This architecture, together with the Achieving Sub‑800 ms Voice AI Latency report and the LiveKit–Exotel quickstart, provides a solid foundation for building scalable, low‑latency voice AI agents.
[1] Voice AI agents compared on latency: performance benchmark
https://telnyx.com/resources/voice-ai-agents-compared-latency
[2] Exotel introduces real-time voice streaming API for AI developers
[3][7] Agents telephony integration | LiveKit Documentation
https://docs.livekit.io/frontends/telephony/agents/
[4] Speech-to-Text in Conversational AI | Comparing Deepgram, Gladia, Whisper and More
https://zoice.ai/blog/speech-to-text-in-conversational-ai/
[5] ElevenLabs vs OpenAI TTS: Which One”s Right for You? – Vapi AI Blog
ElevenLabs vs OpenAI TTS: Which One”s Right for You? – Vapi AI Blog
[6] how-to-setup-exotel-livekit-trunking : Exotel Support Center
how-to-setup-exotel-livekit-trunking
[8] Twilio vs Exotel 2025: Which is Better for India? (Pricing + Features) | edesy.in